Wild Lettuce is a Natural Remedy for Headaches, Insomnia & More

Have you ever considered using wild lettuce?
Wild Lettuce was known to the Egyptians and the ancient Greeks for its ability to calm the mind and body.
Ironically, while the Egyptians thought it would heighten the sexual appetite, Greek priests used the herb to suppress their sexual urges.
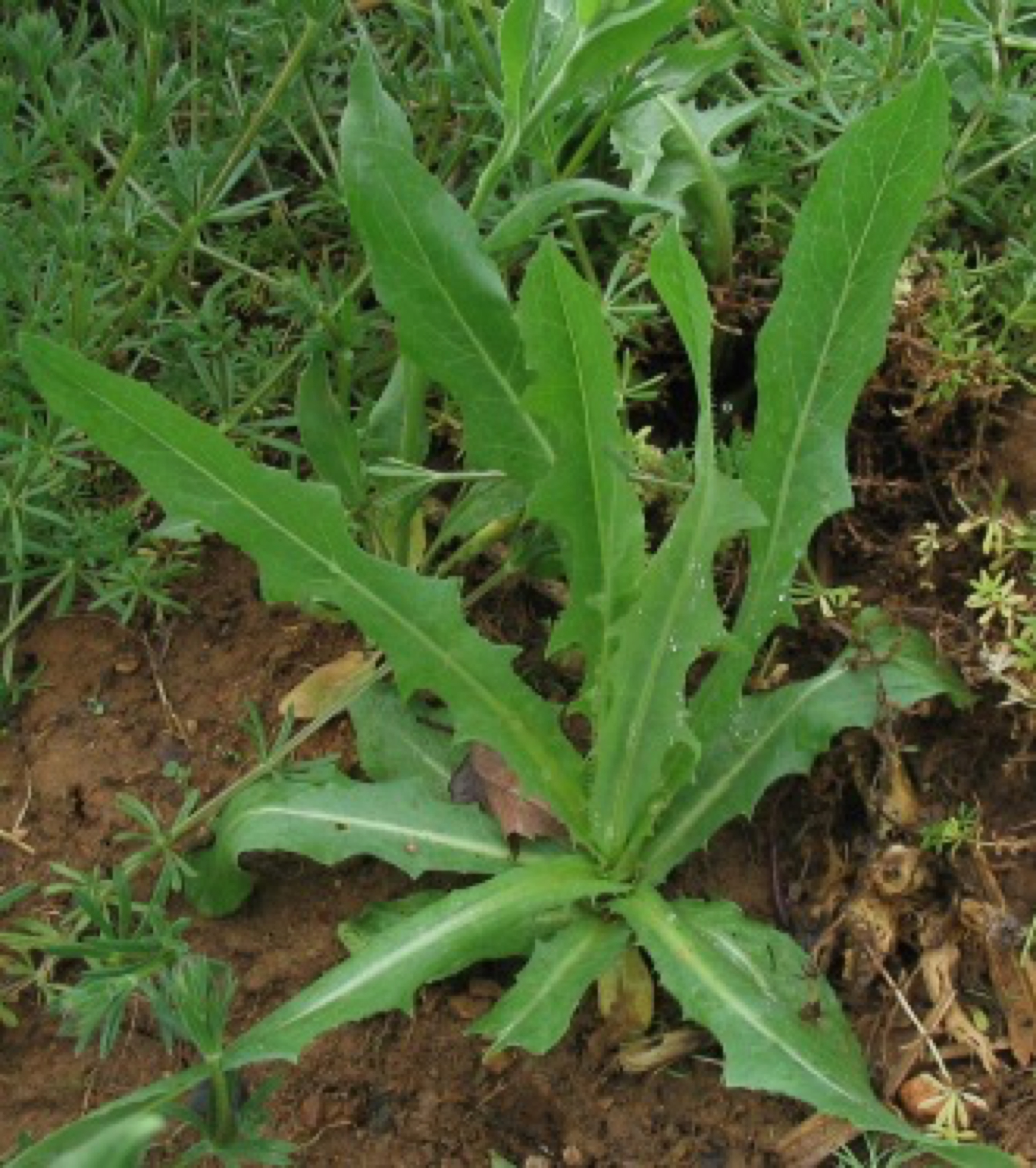
Wild lettuce has a scientific name and it is Lactuca Virosa. But its common name is bitter lettuce or opium lettuce. This leafy and tall plant with small yellow buds is commonly found in North America and England, being a cousin to regular lettuce.
Often known as opium lettuce
The name opium lettuce arose because of its pain relieving and sedative effects. Such effects are produced because of a white substance found in the stem and leaves.
This milky substance is called lactucarium. And, while it doesn’t contain any opiates, it has similar side effects when used. Lactucarium will work on the central nervous system to lessen the feeling of pain - in much the same way as morphine does.
Although not well known today, it has a history of being used as a more natural alternative to pain relief - and even as a recreational substance. In the past, it was prepared in two different ways. One was to cook the plant in a mixture of water and sugar in a pan, reducing it to a thick, syrupy but rather bitter mixture. The other was to dry the stem and leaves to make an herbal tea. But probably the easiest is to buy your own supply of wild lettuce leaf tea.
Some of the conditions where wild lettuce can help
- Reducing the frequency of migraines.
- Producing a relaxed and even euphoric to help non sleepers who suffer from insomnia.
- Acting as a mild sedative for those suffering from anxiety or stress.
- The anti-tussive properties of wild lettuce can alleviate or suppress coughs and relieve asthma.
Of course, Healing Natural Oils can help with other natural remedies for headaches and migraines, and insomnia.
Sources
Digre KB.Headaches and other head pain. In: Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 25th ed. Philadelphia, Pa.: Saunders Elsevier http://www.clinicalkey.com. (Accessed, Feb 13, 2021)
Secondary headaches. American Headache Society Committee for Headache Education. http://www.achenet.org/resources/secondary_headaches/. (Accessed, Feb 13, 2021)
Wong ET, et al. Clinical presentation and diagnosis of brain tumors. http://www.uptodate.com/home. (Accessed, Feb 13, 2021).